Step
Camel supports the Pipes and Filters from the EIP patterns in various ways.
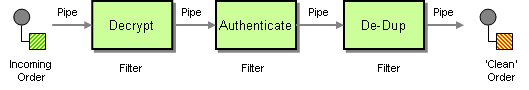
With Camel, you can group your processing across multiple independent EIPs which can then be chained together in a logical unit, called a step.
A step groups together the child processors into a single composite unit. This allows capturing metrics at a group level which can make management and monitoring of Camel routes easier by using higher-level abstractions. You can also think this as a middle-level between the route and each processor in the routes.
You may want to do this when you have large routes and want to break up the routes into logical steps.
This means you can monitor your Camel applications and gather statistics at 4-tiers:
-
context level
-
route(s) level
-
step(s) level
-
processor(s) level
-
-
-
Options
The Step eip supports 1 options, which are listed below.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
description | Sets the description of this node. | String | |
disabled | Whether to disable this EIP from the route during build time. Once an EIP has been disabled then it cannot be enabled later at runtime. | false | Boolean |
outputs | Required | List |
Exchange properties
The Step eip supports 1 exchange properties, which are listed below.
The exchange properties are set on the Exchange by the EIP, unless otherwise specified in the description. This means those properties are available after this EIP has completed processing the Exchange.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
CamelStepId | The id of the Step EIP. | String |
Using Step EIP
In Java, you use step to group together sub nodes as shown:
from("activemq:SomeQueue")
.step("foo")
.bean("foo")
.to("activemq:OutputQueue")
.end()
.to("direct:bar");As you can see this groups together .bean("foo") and .to("activemq:OutputQueue") into a logical unit with the name foo.
In XML, you use the <step> tag:
<route>
<from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/>
<step id="foo">
<bean ref="foo"/>
<to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/>
</step>
<to uri="direct:bar"/>
</route>You can have multiple steps:
-
Java
-
XML
-
YAML
from("activemq:SomeQueue")
.step("foo")
.bean("foo")
.to("activemq:OutputQueue")
.end()
.step("bar")
.bean("something")
.to("log:Something")
.end()<route>
<from uri="activemq:SomeQueue"/>
<step id="foo">
<bean ref="foo"/>
<to uri="activemq:OutputQueue"/>
</step>
<step id="bar">
<bean ref="something"/>
<to uri="log:Something"/>
</step>
</route>- route:
from:
uri: activemq:SomeQueue
steps:
- step:
id: foo
steps:
- bean:
ref: foo
- to:
uri: activemq:OutputQueue
- step:
id: bar
steps:
- bean:
ref: something
- to:
uri: log:Something